$po Function
Syntax
Arguments
- elementelement|string
The DOM element to position. The "position" attribute for the element must be set to absolute, otherwise the $po function cannot be used to position the element.
- parentElementelement|string
The DOM element that is used to calculate the relative position.
- typenumber|string
Defines where you would like the child element to be positioned relatively to the parent element. It can either be a number (see image below), or one of the following keywords:
- dropdown
Positions the child element relative to the bottom left corner of the parent object. (Will position above if there is insufficient space below the parent object.)
- dropdown-right
Positions the child element relative to the bottom right corner of the parent object. (Will position above if there is insufficient space below the parent object.)
- flyout
Positions the child element so that the left side of the child object is positioned relative to the top, right side of the parent object. (Will position left of parent if there is insufficient space to the right of the parent object.)
- flyout-bottom
Positions the child element so that the left side of the child object is positioned relative to the bottom, right side of the parent object. (Will position left of parent if there is insufficient space to the right of the parent object.)
- mainOffsetnumber
Allow you to optionally tweak the positioning of the element by specifying an offset (in pixels) from the element's default position.
- subOffsetnumber
Allow you to optionally tweak the positioning of the element by specifying an offset (in pixels) from the element's default position.
Description
Positions one element relatively to another.
Discussion
The $po() function positions one element relatively to another. The first parameter in the element you wish to position.
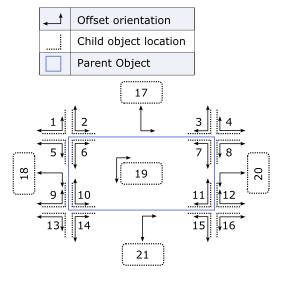
In the image below, the blue box represents that element that you are positioning relative to. There are 21 different numbered position shown on the image. For example, position 1 will position relative to the top left corner of the element. Position 8 will position relative to the top right corner of the element. Position 20 will position centered on the height of the element on the right edge of the element.
The named positions (e.g. 'dropdown', 'flyout', etc.) will take page size into account, and automatically change the positioning of the element if there is not enough room.
The image below also shows the offset orientation. The longer offset orientation arrow represents the main offset, and the short arrow represents the sub offset. So for example, if you specify position 1, with a MAINOFFSET of 10, the right edge of the element that is being moved will be 10 pixels away from the left edge of the element you are positioning relative to. If you specify a SUBOFFSET of -5, then the bottom of the element you are positioning will be 5 pixels closer than normal to the top of the element you are positioning relative to.
Examples:
/*Position an element directly over another element.
Assume that 'overlay' is some object, perhaps a DIV with a transparent fill.
Assume that 'parentObject' is the object that you want to cover with some other object.
We want to position the overlay relative to the top left corner (position 6 in the diagram) of the parent object.
*/
$po('overlay','parentObject',6);
/*Position an element directly over another element and resize the overlay object so that it is the same size as the parent object.*/
$po('overlay','parentObject',6);
$sor('overlay','parentObject','wh');
/*Position an object as a 'dropdown' (position 14). However, if there is not sufficient space for the dropdown object below the parent object, then automatically use position 2.*/
$po('dropdownList','parentObject','dropdown');
/*Position an object below the parent object and centered in the width of the parent object.*/
$po('dropdownList','parentObject',21);
/*Position an object 20 pixels below the parent object and 10 pixels to the left of the center of the parent object.*/
$po('dropdownList','parentObject',21,20,-10);See Also