Date and Time Functions
- *add_days Function
- *add_hours Function
- *add_minutes Function
- *add_months Function
- *add_seconds Function
- *add_years Function
- *days_between Function
- *hours_between Function
- *minutes_between Function
- *months_between Function
- *seconds_between Function
- *years_between Function
- a5_add_timestamp Function
- A5_CONVERT_DATE_STRING Function
- A5_CONVERT_DATETIME_STRING Function
- a5_embeddedcalendargenie Function
- a5_get_date_format Function
- A5_GETDATEHTML Function
- a5_gettimeformats Function
- a5_gettimevalue Function
- a5_normalizedate Function
- A5_RFC1123DATE Function
- A5_RFC822DATE Function
- A5_RFC850DATE Function
- A5_T_FROM_RFCDATE Function
- a5_time_format_help Function
- A5_TIMESTAMP Function
- ADD_BUS_DAYS Function
- ADDMONTHS Function
- ADDYEARS Function
- AGE Function
- BUS_DAYS_BETWEEN Function
- connectionString
- table
- column
- filterColumn
- filterColumnType
- filterValue
- CDATE Function
- CDOW Function
- CMONTH Function
- CONVERT_TYPE Function
- CShortTime Function
- CTIME Function
- CTOD Function
- CTODT Function
- CTOT Function
- CYEAR Function
- Date and Time Conversion Matrix
- Date Input
- Date String Input
- Time Input
- Time String Input
- Short Time Input
- Short Time String Input
- Overview
- Arithmetic
- Calendars
- General
- Calculation Functions
- Conversion Functions
- Formatting Functions
Description
Methods to support date and time data types.
*add_days Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timeTime
A time value.
- daysNumeric
The number of days to add to the time value. Days can be a negative value.
Returns
- newTimeTime
Returns the time value incremented by days.
Description
Add days to date or time.
Example
dim time as t time = now() ? time = 10/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am dim increment as n increment = round(rand()*100,0) ? increment = 29 ? *add_days(time, increment) = 11/10/2017 08:54:05 89 am
See Also
*add_hours Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timeTime
A time value.
- hoursNumeric
The number of hours to add to the time value. Hours can be a negative value.
Returns
- newTimeTime
Returns the time value incremented by hours.
Description
Add hours to date or time.
Example
dim time as t time = now() ? time = 10/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am dim increment as n increment = round(rand()*100,0) ? increment = 9 ? *add_hours(time, increment) = 10/12/2017 05:54:05 89 pm
See Also
*add_minutes Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timeTime
A time value.
- minutesNumeric
The number of minutes to add to the time value. Minutes can be a negative value.
Returns
- newTimeTime
Returns the time value incremented by minutes.
Description
Add minutes to date or time.
Discussion
The *add_minutes() function increments a time value by a specified number of minutes.
Example
dim time as t time = now() ? time = 10/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am dim minutes as n minutes = round(rand()*100,0) ? minutes = 99 ? *add_minutes(time, minutes) = 10/12/2017 10:33:05 89 am
Example: Ajax Callback in a UX
The example below is an Ajax Callback for a UX Component with 3 text boxes with a T (time) type. The callback calculates two reminders based on the time value in the 'ScheduledTime' control. The resulting reminder values are set in the 'Reminder1' and 'Reminder2' text controls in the UX.
function calculateReminders as c (e as p)
' Get the submitted time value:
dim time as T = convert_type(e.dataSubmitted.ScheduledTime,"T")
' Compute the time for the 2 reminders: 15 and 30 minutes prior:
dim reminder1 as T = *add_minutes(time,-30)
dim reminder2 as T = *add_minutes(time,-15)
' Set the value for the reminder textboxes in the UX
' Note: Must convert the time value to a string with the format
' matching the time format used in the controls.
e._set.reminder1.value = time("MM/dd/yyyy 0h:0m am",reminder1)
e._set.reminder2.value = time("MM/dd/yyyy 0h:0m am",reminder2)
' Return optional JavaScript here:
calculateReminders = ""
end functionSee Also
*add_months Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timeTime
A time value.
- monthsNumeric
The number of months to add to the time value. Months can be a negative value.
Returns
- newTimeTime
Returns the time value incremented by months.
Description
Add months to date or time.
Example
dim time as t time = now() ? time = 10/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am dim increment as n increment = round(rand()*100,0) ? increment = 2 ? *add_months(time, increment) = 12/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am
See Also
*add_seconds Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timeTime
A time value.
- secondsNumeric
The number of seconds to add to the time value. Seconds can be a negative value.
Returns
- newTimeTime
Returns the time value incremented by seconds.
Description
Add seconds to date or time.
Example
dim time as t time = now() ? time = 10/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am dim increment as n increment = round(rand()*100,0) ? increment = 29 ? *add_seconds(time, increment) = 10/12/2017 08:54:34 89 am
See Also
*add_years Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timeTime
A time value.
- yearsNumeric
The number of years to add to the time value. Years can be a negative value.
Returns
- newTimeTime
Returns the time value incremented by years.
Description
Add years to date or time.
Example
dim time as t time = now() ? time = 10/12/2017 08:54:05 89 am dim increment as n increment = round(rand()*100,0) ? increment = 29 ? *add_years(time, increment) = 10/12/2046 08:54:05 89 am
See Also
*days_between Function
Syntax
Arguments
- t1Time
A datetime value.
- t2Time
A datetime value
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns the days between the specified datetime values. If t2 is a date later than t1, *DAYS_BETWEEN will return a negative value.
Description
Return difference of days between two dates or times.
Example
dim t1 as T
dim t2 as T
dim t3 as T
t1 = {01/12/2016}
t2 = {01/24/2016}
t3 = {01/08/2016}
? *days_between(t2, t1)
= 12
? *days_between(t3, t1)
= -4See Also
*hours_between Function
Syntax
Arguments
- t1Time
A datetime value.
- t2Time
A datetime value
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns the hours between two dates or times. If t2 is a date or time later than t1, *HOURS_BETWEEN will return a negative value.
Description
Return difference of hours between two dates or times.
Example
dim time1 as t = now() dim time2 as t = *add_hours(time1, 9) ? *hours_between(time2, time1) = 9 ? *hours_between(time1, time2) = -9
See Also
*minutes_between Function
Syntax
Arguments
- t1Time
A datetime value.
- t2Time
A datetime value
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns the minutes between two dates or times. If t2 is a date or time later than t1, *MINUTES_BETWEEN will return a negative value.
Description
Return difference of minutes between two dates or times.
Example
dim t1 as t = now() dim t2 as t = earlier ? t1 = 10/12/2017 11:32:53 53 am ? t2 = 10/12/2017 09:12:44 65 am ? *minutes_between(t2, t1) = -140.147966666667
See Also
*months_between Function
Syntax
Arguments
- t1Time
A datetime value.
- t2Time
A datetime value
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns the months between two dates or times. If t2 is a date or time later than t1, *MONTHS_BETWEEN will return a negative value.
Description
Return difference of months between two dates or times.
Example
dim cn as sql::Connection
cn.open("::Name::northwind")
dim args as sql::arguments
args.set("orderID",10251)
dim sql as c = "SELECT * FROM orders WHERE orderid = :orderID"
cn.execute(sql,args)
if (cn.ResultSet.NextRow()) then
dim t1 as T = cn.resultset.data("requireddate")
dim t2 as T = cn.resultset.data("shippeddate")
dim months_between as N = *months_between(t1,t2)
months_between = abs(months_between)
dim timing as c = ""
if (t2 > t1) then
timing = "late"
else
timing = "early"
end if
ui_msg_box("Months Between","Order 10251 was shipped " + months_between + " month " + timing + crlf(2) + "Required date: " + time("MM/dd/yyyy",t1) + crlf() + "Shipped date: " + time("MM/dd/yyyy", t2))
end if
cn.close()See Also
*seconds_between Function
Syntax
Arguments
- t1Time
A datetime value.
- t2Time
A datetime value
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns the seconds between two dates or times. If t2 is a date or time later than t1, *SECONDS_BETWEEN will return a negative value.
Description
Return difference of seconds between two dates or times.
Example
dim now as t = now() ' wait a few seconds before typing the following into the interactive window: dim someTimeLater as t = now() ? now = 10/12/2017 11:47:06 82 am ? someTimeLater = 10/12/2017 11:47:16 58 am ? *seconds_between(someTimeLater, now) = 9.759
See Also
*years_between Function
Syntax
Arguments
- t1Time
A datetime value.
- t2Time
A datetime value
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns the years between two dates or times. If t2 is a date or time later than t1, *YEARS_BETWEEN will return a negative value.
Description
Return difference of years between two dates or times.
Example
dim birthDate as t = convert_type({01/20/1981},"T")
dim now as t = now()
dim age as n = *years_between(now, birthDate)
? age
= 36See Also
a5_add_timestamp Function
Syntax
Arguments
- input_script_text
Character
Description
Adds a date and time stamp to a script or function when it is saved
See Also
A5_CONVERT_DATE_STRING Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateStringCharacter
The original data string, containing values for year, month, and day. Character
- InDateFormatCharacter
A character string containing the letters "Y", "M", and "D" that indicates the sequence of input values.
- OutDateFormatCharacter
A character string containing the letters "Y", "M", and "D" that indicates the sequence of output values.
- separatorCharacter
The character(s) to place between the year, month, and day values.
Returns
- Output_DateCharacter
The reformatted date string.
Description
The A5_CONVERT_DATE_STRING() function reformats a date string, by converting a date string from one format to another. E.g. from DMY format to YMD format.
Example
? a5_convert_date_string("12/31/05", "MDY", "YMD", "-")
= "05-12-31"See Also
A5_CONVERT_DATETIME_STRING Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateTimeStringCharacter
The original data string, containing values for year, month, day, hours, and minutes.
- InDateFormatCharacter
A character string containing the letters "Y", "M", and "D" that indicates the sequence of input values.
- OutDateFormatCharacter
A character string containing the letters "Y", "M", and "D" that indicates the sequence of output values.
- separatorCharacter
The character(s) to place between the year, month, and day values.
Returns
- Output_Date_TimeCharacter
The reformatted date time string.
Description
The A5_CONVERT_DATETIME_STRING() function reformats a date portion of a date time string, by converting a datetime string from one format to another. E.g. from DMY format to YMD format.
Example
? a5_convert_datetime_string("12/31/05 4:12pm", "MDY", "YMD", "-")
= "05/12/31 4:12pm"See Also
a5_embeddedcalendargenie Function
Syntax
Arguments
- pedit
Pointer
Description
Display the datePicker genie
See Also
a5_get_date_format Function
Syntax
Description
Determines if the default date format is 'm/d' - USA format, or 'd/m' - non USA format.
See Also
A5_GETDATEHTML Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Selected_Date
The date selected by the user.
- title
Optional. Default = "Calendar". The title of the calendar dialog.
- default_date
Optional. Default = current date. The initial date to show selected in the calendar.
- style
Optional. The path to and filename of a CSS style.
- nocaption
Logical
- xdialogPositionCommand
Character
Description
Displays a dialog with a popup calendar rendered using HTML.
Discussion
The A5_GETDATEHTML() function displays an HTML calendar and returns a date value formatted as a character string. The range of years shown is from 1950 to 2050. Note : If you have changed the Xdialog system font setting from its default value, you should use HTML style display. To enable HTML style display, select View > Settings > System > Preferences > Calendar Popup. Select Style and a cascading style sheet from the Value list. If you use the Xdialog style, you should have your Xdialog system font setting at its default value (Tahoma 8 point). To restore the default font setting select View > Settings > System > System Fonts > Restore Default. These settings also affect POPUP.CALENDAR()and UI_GET_DATE_CALENDAR().
Example
? A5_GETDATEHTML("","","")
= "11/15/2004"Limitations
Desktop applications only.
See Also
a5_gettimeformats Function
Syntax
Arguments
- type
Character
Description
Get the time format strings
See Also
a5_gettimevalue Function
Syntax
Arguments
- time
Character
Description
Prompt for a time value
See Also
a5_normalizedate Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateC
Character
- format
Character
- displayUnformat
Character
Description
Used to normalize a character date or date/time value so that it conforms to local regional settings. You can specify an optional 'switch year' in the format: e.g. mm/dd/yy::30.
See Also
A5_RFC1123DATE Function
Syntax
Formatted_Date_Time as C = a5_rfc1123date(* date )
Formatted_Date_Time as C = A5_RFC1123DATE( Character_Date as C )
Formatted_Date_Time as C = A5_RFC1123DATE( Time_Date_Value as T )
Arguments
- Formatted_Date_Time
A date time value in the format: "Day, dd Mon yyyy hh:mm:ss GMT " ("Tue, 30 Mar 2004 14:17:02 GMT")
- Character_Date
A date time value formatted "mm/dd/yyyy 0h:0m:0s am".
- date
*
- Time_Date_Value
A date time value.
Description
Converts a date string to an RFC 1123 formatted date (Day, dd Month yyyy hh:mm:ss TIMEZONE)
Discussion
The A5_RFC1123DATE() function takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string following the RFC 1123 format.
Example
dim t as T t = now() ? a5_rfc1123date(t) = "Tue, 30 Mar 2004 16:17:55 GMT"
See Also
A5_RFC822DATE Function
Syntax
Formatted_Date_Time as C a5_rfc822date(* date )
Formatted_Date_Time as C = A5_RFC822DATE( Character_Date_Time as C )
Formatted_Date_Time as C = A5_RFC822DATE( Time_Date as T )
Arguments
- Formatted_Date_Time
A date time value in the format: "Day, dd Mon yy hh:mm:ss GMT " ("Tue, 30 Mar 04 14:17:02 GMT")
- Character_Date_Time
A date time value formatted "mm/dd/yyyy 0h:0m:0s am".
- date
A date time value.
Description
Converts a date string to an RFC 822 formatted date (Day, dd Month yy hh:mm:ss TIMEZONE)
Discussion
The A5_RFC822DATE() function takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string following the RFC 822 format.
Example
dim t as T t = now() ?a5_rfc822date(t) = "Tue, 30 Mar 04 16:17:55 GMT"
See Also
A5_RFC850DATE Function
Syntax
Formatted_Date_Time as C = a5_rfc850date(* date )
Formatted_Date_Time as C = A5_RFC850DATE( Character_Date_Time as C )
Arguments
- Formatted_Date_Time
A date time value in the format: "Weekday, dd-Mon-yy hh:mm:ss GMT" ("Tuesday, 30-Mar-04 14:17:02 GMT")
- Character_Date_Time
A date time value formatted "mm/dd/yyyy 0h:0m:0s am".
- date
A date time value.
Description
Converts a date string to an RFC 850 formatted date (Weekday, dd-Mon-yy hh:mm:ss TIMEZONE)
Discussion
The A5_RFC850DATE() function takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string following the RFC 850 format.
Example
dim t as T t = now() ? a5_rfc850date(t) = "Tuesday, 30 Mar 04 16:17:55 GMT"
See Also
A5_T_FROM_RFCDATE Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Date_Time_Value
A date time value in the format: 03/30/0004 04:17:55 00 pm
- date_string
A formatted date. Character
Description
Converts a time in RFC 822, RFC 850, RFC 1123 or ANSI C format to a time variable
Discussion
The A5_T_FROM_RFCDATE() function converts a date time string in RFC 822, RFC 850, RFC 1123 or ANSI C formats to a Time variable. This function will automatically determine the format of the input string and handle the conversion appropriately.
Example
dim t as T t = now() ? a5_t_from_rfcdate(a5_rfc822date(t)) = 03/30/0004 04:17:55 00 pm ? a5_t_from_rfcdate(a5_rfc850date(t)) = 03/30/0004 04:17:55 00 pm ? a5_t_from_rfcdate(a5_rfc1123date(t)) = 03/30/2004 04:17:55 00 pm ? a5_t_from_rfcdate(a5_ansidate(t)) = 03/30/2004 11:17:55 00 am
See Also
a5_time_format_help Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date_only
Logical
- time_only
Logical
- initialValue
Character
- flagSuppressMilliseconds
Logical
Description
Builder for time/date format string.
See Also
A5_TIMESTAMP Function
Syntax
Returns
- Formatted_Short_TimeCharacter
The current system time formatted according to your preferences.
Description
Generates a timestamp as a character string for the current time.
Discussion
The A5_TIMESTAMP() function returns a short time value as character string, using the time format specified in the Settings dialog box ( Settings... > Preferences > Time ) section. This function is called when the user presses the Control + Shift + T hotkey in form or browse mode.
Example
? a5_timestamp() = "04:51 PM"
See Also
ADD_BUS_DAYS Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Ending_Date
The resulting date.
- startDate
The starting date to which you will add business days.
- AddDays
A positive or negative number ( not zero). The number of business days to add or subtract. The function does not count weekend days.
- flag
Optional. Default = "". If Ignore_Holiday_Flag is any non-null value, the function subtracts holidays from the number of non-weekend days.
- holidayTable
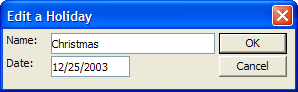
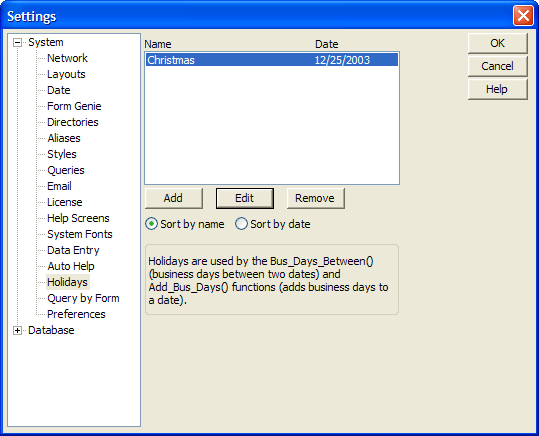
Optional. Default = "a_holidays.dbf". If Ignore_Holiday_Flag is "yes", the function uses the list of holidays is supplied in Holiday_Table. If Holiday_Table is blank, then Alpha Anywhere uses the "a_holidays.dbf" table which is contained in the Alpha Anywhere program folder. The holidays in the "a_holidays.dbf" table are defined in the Settings dialog box, accessed with the View > Settings > System > Holidays command from the Alpha Anywhere menus.
Description
ADD_BUS_DAYS() returns an Ending_Date equal to Starting_Date plus Add_Days number of business days.
Adds business days to a date, ignoring weekends. AddDays can be positive or negative. If flag is "yes", then holidays are also ignored. If holidayTable is not specified, then default holiday table (see View/Settings) is used. To use a SQL datasource, 'holidayTable' can be a JSON string with these properties: connectionString, table, column. e.g. {connectionString: 'northwind', table: 'holidays', column: 'dates'}
Example
? {7/12/2002} + 1
= {7/13/2002}
? add_bus_days({7/12/2002}, 1)
= {07/15/2002}See Also
ADDMONTHS Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateDate
The date that months will be added to.
- monthsDate
The number of months to add. Specifying a negative value will perform a month subtraction from the specified date.
Returns
- Ending_DateDate
The result of adding months to date.
Description
Adds a number of months to a date.
Discussion
ADDMONTHS() returns an Ending_Date equal to the specified Starting_Date plus the specified Number_Of_Months.
The ADDMONTHS() function adds the specified Number_Of_Months to the Starting_Date and then checks if the resulting date is valid. If the resulting date is not valid (e.g., 1-31-95 plus 1 month is 2-31-95), the highest valid date in that month (e.g., 2-28-95) is returned. Alpha Anywhere does recognize leap years.
Example
? ADDMONTHS({1-31-95},1)
= {02/28/1995}
? ADDMONTHS({3-15-95},1)
= {04/15/1995}
? ADDMONTHS({5-15-95},-2)
= {03/15/1995}See Also
ADDYEARS Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
The date to which you will add business days.
- years
The number of years to add.
Description
Adds a number of years to a date.
Discussion
ADDYEARS() returns an Ending_Date equal to Date plus the specified Number_Of_Year s. The ADDYEARS() function works by adding the specified Number_Of_Year s to the Starting_Date and then checking if the resulting date is valid. If the resulting date is not valid (e.g., 2-29-92 plus 1 year is 2-29-93), Alpha Anywhere returns the next valid day (e.g., 3-1-93).
Example
? addyears({2-28-92},1)
= {02/28/1993}
? addyears({2-29-92},1)
= {03/01/1993}See Also
AGE Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dob
The first date.
- AsOfDate
Optional. Default = DATE(). The second date to use in calculating the age.
Description
Computes a person's age. If AsOfDate is not supplied, then age as of today is computed. If AsOfDate is supplied, then age on the AsOfDate is computed.
Discussion
AGE() returns the integer number of years between Starting_Date and Ending_Date (default now).
Example
age({12/18/1952}) -> 49See Also
BUS_DAYS_BETWEEN Function
Syntax
Arguments
- startDate
The date to which you will add business days.
- endDate
The number of business days to add. The function does not count weekend days.
- flag
Default = "". If Ignore_Holiday_Flag is any non-null value, the function subtracts holidays from the number of non-weekend days.
- holidayTable
Optional. Default = "a_holidays.dbf". If Ignore_Holiday_Flag is non-null, the function uses the list of holidays supplied in Holiday_Table. If Holiday_Table is blank, then Alpha Anywhere uses the a_holidays.dbf table which is contained in the Alpha Anywhere program folder. The holidays in the a_holidays.dbf table are defined in the Settings dialog box, accessed with the View > Settings > System > Holidays command from the Alpha Anywhere menus.
Description
BUS_DAYS_BETWEEN() returns the number of business days between two dates, ignoring weekends and holidays. To use a SQL datasource, 'holidayTable' can be a JSON string with these properties: connectionString, table, column. e.g. {connectionString: 'northwind', table: 'holidays', column: 'dates'}
Example
? bus_days_between({1/18/1948}, date() , "yes")
= 14348The following scripts count the number of business days in the month that contains a specific date.
dim num_days as N
dim dd as D
dd = date()
num_days = bus_days_between(month_start({2/26/06}), month_end({2/26/06}))
num_days = bus_days_between(month_start(dd), month_end(dd))SQL 'Holidays' Table
The Bus_days_between() can use a SQL table as the data source for the list of holiday dates. To specify a SQL table, the 'holidayTable' argument that is passed into the function is in the form of a JSON string with these properties:
connectionString
The connection string to the SQL database
table
The name of the table that contains the holiday dates. If this property is not specified a table called 'A5Holidays' is assumed.
column
The name of the column that contains the holiday dates. If this property is not specified, a column called 'Dates' is assumed.
filterColumn
(optional) the name of a column in the holiday table that you want to filter on
filterColumnType
(required if filterColumn is specified) - the data type of the filterColumn. Can be c,n,d,t,l.
filterValue
(required if filterColumn is specified) - the value to search for.
Example:
days = Bus_days_between( {12/1/2013},{12/31/2013},"yes","{connectionstring:
'myconnstring', table: 'holidays', column: 'dates'}")
days = Bus_days_between( {12/1/2013},{12/31/2013},"yes","{connectionstring:
'myconnstring', table: 'holidays', column: 'dates', filterColumn: 'country',
filterColumnType: 'c', filterValue: 'USA'}")See Also
CDATE Function
Syntax
C CDATE(D date)
Formatted_Date as C = CDATE( date as D )
Formatted_Date as C = CDATE( date_time as T )
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
- date-time
A variable containing a date time value.
Description
Converts a date to a character value in the form 'YYYYMMDD'.
Discussion
CDATE() interprets a Date value and returns a Formatted_Date character string in the form "YYYYMMDD". This function is useful for constructing multi-level indexes that contain both character and date fields. Indexes containing the CDATE() function order dates chronologically (year, then month, then day), while those containing DTOC() order dates by month, day, and year.
Example
? cdate(date() )
= "20050617"
? cdate({6/15/05})
= "20050615"
INV_DATE = {12/18/1993}
? cdate(INV_DATE)
= "19931218"Assume you want to order an employee table by department and within each department by seniority. The table has a character field, DEPT, and a date field, STARTDATE. Use the following index expression:
DEPT + cdate(START)
The following table shows the order created by this index:
- EMPLOYEE
- >
- FIRSTNAME
- DEPT and START DATE
- Steve
Marketing, 03/21/78
- Kate
Marketing, 04/17/79
- Sarah
Marketing, 01/02/83
- Ralph
R&D, 01/01/80
- Tim
R&D 03/20/80
- Francie
R&D 02/17/84
Compare this result with the DTOC() function. If the DTOC() function is used in the above index expression instead of CDATE() , the following ordering results:
- EMPLOYEE
- >
- FIRSTNAME
- DEPT and START DATE
- Sarah
Marketing, 01/02/83
- Steve
Marketing, 03/21/78
- Kate
Marketing 04/17/79
- Ralph
R&D 01/01/80
- Francie
R&D 02/17/84
Entering search criteria to search on a date field presents a problem because you cannot type in a date directly as a text string. You must either surround the text you enter with the CTOD() function, or use a function to convert the date field to a character field before comparing it with the text. If you want to search a date field, BIRTHDAY, for the date, "September 20, 1966," you can enter the following criteria:
cdate(BIRTHDAY) = "19660920" or
BIRTHDAY = ctod("09/20/1966") or
BIRTHDAY = ctod("09/20/66") or
BIRTHDAY = {9/20/66}If you want to test for a blank date, use the following expression:
if (trim(cdate(datevalue) ) = "") then
' blank value code
else
' valid date code
end ifSee Also
CDOW Function
Syntax
Day_of_Week as C = CDOW(D date[,L localized])
Day_of_Week as C = CDOW( D time as T [, localized as L])
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
- time
A variable containing a date time value.
- localized
Logical. A variable containing .T. if a localized date is requested.
Description
CDOW() returns a character string containing the name of the day of the week for the specified Date. If the optional localized flag is true, report the localized day name. (Localized flag requires Version 10.5 or later)
Example
cdow(START) -> "Tuesday", if START contains 11/28/95 cdow( ctod( "05/15/95") ) -> "Monday"
If you print form letters that mention dates in the body of the letter, you may want to create a field containing the day of the week. For example, "I'll see you on Monday" sounds more personal than "I'll see you on 5/15/95." Assume that your table has a date field, APPOINTMNT, which stores the date for a scheduled appointment. You can include a computed field right in the body of the letter; Alpha Anywhere calculates the expression when the letter is printed. For this letter, the expression is:
cdow(APPOINTMNT)
In Version 10.5, this function has an optional second logical parameter to force the function to honor the machine's regional settings when returning the day name, Localized as L.
See Also
CMONTH Function
Syntax
Month_Name as C = CMONTH(D date[,L localized])
Month_Name as C = CMONTH( D time as T[, localized as L] )
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
- time
A variable containing a date time value.
- localized
Logical. A variable containing .T. if a localized month is requested.
Description
CMONTH() returns the Month_Name in the specified Date or Date_Time. If the optional localized flag is true, report the localized day name. (Localized flag requires Version 10.5 or later).
Example
cmonth(START) -> "March", if START contains 03/07/95 cmonth( ctod( "05/25/95") ) -> "May"
See Also
CONVERT_TYPE Function
Syntax
Arguments
- SourceAny Type
A variable containing character, numeric, date, or logical data.
- RequestedTypeCharacter
The requested data type. The type can be any Xbasic type listed below:
- Type
- Description
- C
Character
- D
Date
- K
GUID
- L
Logical
- N
Numeric
- T
Date Time
- Y
Short Time
See Variable Data Types to learn more about Xbasic variable data types.
Returns
- Output_ValueAny Type
Returns the value of Source variable as the requested data type. If the requested type is not supported or doesn't exist, the returned value will be a Character value.
Description
Converts a value from one data type to another.
Discussion
CONVERT_TYPE() converts variables from one data type to another, preserving the data if possible.
? convert_type("yes", "L")
= .T.
? convert_type(345, "C")
= "345"
? convert_type(now(), "C")
= "12/08/2018 02:32:17 27 am"If the requested data type is not supported or invalid, CONVERT_TYPE() converts the value to a Character data type. For example:
' Converting to a dot variable "P" is not supported result1 = convert_type(.F., "P") ' Data returned as type "C": ? typeof(result1) = "C" ? result1 = "False"
See Also
CShortTime Function
Syntax
Arguments
- shorttimeShortime
A short time value. For example: 09:27:16 91 am
Description
The CShortTime() function converts a short time value into a character value (string) that can be used in a sort expression. Format is 0h0m0s3.
Discussion
Returns a character string representation of a short time value that can be sorted. The format is hhmmssP.
Example
dim st as Y st = now() ? st = 09:38:35 80 am ? cshorttime(st) = "093835803"
See Also
CTIME Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Time_Equivalent
A character string representation of a time value that can be sorted. The format is YYYMMDDhhmmssP
- timeval
A time value. For example: 02/15/2006 09:27:16 91 am
Description
The CTIME() function converts a time value into a character value (string) that can be used in a sort expression. Format is YYYYMMDD0h0m0s3.
Discussion
Example
? ctime(now() ) = "20060215092839365" dim tt as T dim na as C = "Fred" tt = now() ? tt = 02/15/2006 09:27:16 91 am ? na + ctime(tt) = "Fred20060215092716912"
See Also
CTOD Function
Syntax
Arguments
- character
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( < span class=Code1>ISDATE (Date_Representation) = .T. ).
Description
Converts a character string to a date value.
Discussion
CTOD() returns a Date value extracted from a character string. For more information about date formats, see the DATE_FORMAT()function. The two most frequent uses of CTOD() are: searching and filtering date fields, and converting character fields containing dates into real date fields. Note : If the setting for Fully Specified Years requires all dates to be fully specified CTOD returns a blank value for years specified as 2 numbers.
Assume that you just re-configured an existing table to add a new date field called START_DATE. This field is initially blank for all the records, so you want to put the date "12/12/95" in all the records. Instead of editing each record individually, use the Update builder to update all of the records at once with an operation. You can define the following update expression for START_DATE:
ctod("12/12/95")The quotation marks are necessary to indicate that the data inside the parentheses is character data. CTOD converts the character date string to a date field type so that you can insert it into START_DATE. Note : A convenient alternative to CTOD() is enclosing the date values (without quotation marks) in curly brackets (e.g., {12/12/95}).
See Also
CTODT Function
Syntax
Arguments
- character
A character string containing a legitimate representation of a date time value.
Description
The CTODT() function converts a date and time string to a Date Time value (date + time).
Example
? ctodt("1/23/2003 11:45")
= 01/23/2003 11:45:00 00 am
? ctodt(dtoc(date() ) + " " + time() )
= 11/04/2003 03:57:00 00 pmAs of Version 10.5, if the 'am' or 'pm' flag is left out, Alpha Anywhere now assumes that the user is specifying a time using a 24 hour format. Previously, a time value of '00:00:00' was considered to be invalid. Now this is a valid 24 hour format time value.
See Also
CTOT Function
Syntax
Arguments
- character
A character string containing a legitimate representation of a short time value.
Description
The CTOT() function converts a time string to a Short Time value.
Example
dim tc as C
tc = time()
? tc
= "15:47:05"
? ctot(tc1)
= 03:47:05 00 pm
? ctot("2:30 pm")
= 02:30:00 00 pmSee Also
CYEAR Function
Syntax
Year_String as C = CYEAR(D date)
Year_String as C = CYEAR( D time as T )
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
A variable containing a date time value.
Description
Converts a date to a character value of the form 'YYYY'.
Discussion
CYEAR() returns a character string (in the format "YYYY") containing the year specified in Date or Date_Time. You can combine the CYEAR() , CMONTH() , CDOW() , and DAY() functions to form custom date formats. For examples, see the DAY() function.
Example
cyear(START) -> "1995", if START contains 03/12/95 cyear( ctod( "05/19/94") ) -> "1994"
See Also
Date and Time Conversion Matrix
Description
A list of Inputs and Outputs relating to date time functions.
Date Input
Symbol D
Output Type
Now
- Symbol
D
- Function
DATE()
Date String
- Symbol
C
- Function
DTOC( Date_Value )
Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
YEAR( Date_Value )
Month
- Symbol
C
- Function
DATE_FORMAT( Date_Value, "Month")
Month of Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
MONTH( Date_Value )
Week of Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
WEEK( Date_Value )
Day
- Symbol
C
- Function
DATE_FORMAT( Date_Value, "Weekday")
Last Date of Month
- Symbol
D
- Function
MONTH_END( Date_Value )
Day of Month
- Symbol
N
- Function
DAY( Date_Value )
Day of Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
JDATE( Date_Value ) - JDATE(CTOD("1/1/" + YEAR( Date_Value ))) + 1
Days
- Symbol
N
- Function
Date_Value1 - Date_Value2
Business Days in Month
- Symbol
N
- Function
BUS_DAYS_BETWEEN(MONTH_STARTt( Date_Value ), MONTH_END( Date_Value ))
Sortable Date Value
- Symbol
C
- Function
CDATE( Date_Value )
Time Input
Symbol T.
Output Type
Now
- Symbol
T
- Function
NOW()
Time
- Symbol
C
- Function
TIME("", Time_Variable )
Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
YEAR( Time_Variable )
Month of Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
MONTH( Time_Variable )
Week of Year
- Symbol
N
- Function
WEEK(DATE_VALUE(YEAR( Time_Variable ), MONTH( Time_Variable ), DAY( Time_Variable )))
Day of Month
- Symbol
N
- Function
DAY( Time_Variable )
Hour (12)
- Symbol
N
- Function
IF(VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable )) 12, VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable )) - 12, VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable )))
Hour (24)
- Symbol
N
- Function
VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable ))
Minute
- Symbol
N
- Function
VAL(TIME("m", Time_Variable ))
Second
- Symbol
N
- Function
TIME("s", Time_Variable )
Seconds
- Symbol
N
- Function
Time_Variable1 - Time_Variable2
AM/PM
- Symbol
C
- Function
TIME("am", Time_Variable )
Date
- Symbol
D
- Function
DIM Date_Variable as D Date_Variable = Time_Variable
Short Time
- Symbol
Y
- Function
CTOT( Time_Variable )
Character
- Symbol
C
- Function
CTIME( Time_Variable )
Sortable Time Value
- Symbol
C
- Function
CDATE( Time_Variable ) + TIME("hms", Time_Variable )
Short Time Input
Symbol Y.
Output Type
Now
- Symbol
Y
- Function
DIM Short_Time_Variable as Y Short_Time_Variable = NOW()
Hour (12)
- Symbol
N
- Function
DIM Time_Variable as T Time_Variable = Short_Time_Variable IF(VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable )) 12, VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable )) - 12, VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable )))
Hour (24)
- Symbol
N
- Function
DIM Time_Variable as T Time_Variable = Short_Time_Variable VAL(TIME("h", Time_Variable ))
Minute
- Symbol
N
- Function
DIM Time_Variable as T Time_Variable = Short_Time_Variable V AL(TIME("m", Time_Variable ))
Second
- Symbol
N
- Function
DIM Time_Variable as T Time_Variable = Short_Time_Variable TIME("s", Time_Variable )
Seconds
- Symbol
N
- Function
DIM Short_Time_Variable1 as Y DIM Short_Time_Variable2 as Y Short_Time_Variable1 - Short_Time_Variable2
AM/PM
- Symbol
C
- Function
DIM Time_Variable as T Time_Variable = Short_Time_Variable TIME("am", Time_Variable )
Time
- Symbol
T
- Function
DIM Time_Variable as T Time_Variable = Short_Time_Variable
Character
- Symbol
C
- Function
CShortTime( Short_Time_Variable )
Sortable Short Time
- Symbol
C
- Function
TIME("hms", Time_Variable )
Hour (12)
- Symbol
N
- Function
IF(ShortTime_Extract( Short_Time_Variable, "h") > 12, ShortTime_Extract( Short_Time_Variable, "h") - 12, ShortTime_Extract( Short_Time_Variable, "h")
Hour (24)
- Symbol
N
- Function
ShortTime_Extract( Short_Time_Variable, "h")
Minute
- Symbol
N
- Function
ShortTime_Extract( Short_Time_Variable, "m")
Second
- Symbol
N
- Function
ShortTime_Extract( Short_Time_Variable, "s")
AM/PM
- Symbol
C
- Function
IF(shortTime_extract( Short_Time_Variable,"h") > 11, "pm", "am")
See Also
Date and Time Format Elements
Description
A date format is created from the following date format elements.
To include separators in the formatted result, include separators in the format string. For example, "MON, d-yyyy". To use a format code a separator, precede the code with the escape character ("\").
Time formatting defaults to 24 hour time unless otherwise specified in the format.
Element | Description | Example Output |
|---|---|---|
0 | Format element (causes a time element h, m, or s, to be returned with a leading 0). | 01, 08, 06 |
s | Second | 33,5 |
1 | Display fractional seconds to 1 decimal place. | .5 |
2 | Display fractional seconds to 2 decimal places. | .13 |
3 | Display fractional seconds to 3 decimal places. | .599 |
m | Minute | 59,10,9 |
h | Hour | 12, 1 |
a | 12 hour clock with "a" or "p" suffix. | a, p |
am | 12 hour clock with "am" or "pm" suffix | am, pm |
A | 12 hour clock with "A" or "P" suffix | A, P |
AM | 12 hour clock with "AM" or "PM" suffix | AM, PM |
d | day (one digit) | 3 |
dd | day (two digits, 0 pad) | 03, 15 |
x | day with "st", "rd", "th" etc (e.g. 1st, 2nd, 23rd) | 1st, 2nd, 23rd |
X | day spelled out | First, Second, Twenty Third |
W | weekday (three character, upper case) | SUN, MON |
w | weekday (three character, lower case) | sun, mon |
WEEKDAY | weekday (full name, upper case) | SUNDAY, MONDAY |
weekday | weekday (full name, lower case) | sunday, monday |
Weekday | weekday (full name, proper case) | Sunday, Monday |
M | month (one digit) | 1 |
MM | month (two digits, zero pad) | 01, 10 |
MON | month (three character name, upper case) | JAN, FEB |
mon | month (three character name, lower case) | jan, feb |
Mon | month (three character name, proper case) | Jan, Feb |
MONTH | month (full name, upper case) | JANUARY, FEBRUARY |
month | month (full name, lower case) | january, february |
Month | month (full name, proper case) | January, February |
y | year (two digits) | 99, 03 |
yy | year (two digits) | 99, 03 |
yyyy | year (four digits) | 1999, 2003 |
Format Examples
curr = now()
? time("0h:0m",curr)
= "19:14"
? time("0h:0m a",curr)
= "07:14 p"
? time("dd-Month-yyyy",curr)
= "21-June-2021"
? time("Weekday, Mon dd, h:m am",curr)
= "Monday, Jun 21, 7:14 pm"
? time("X Weekday of Month",curr)
= "Twenty First Monday of June"
? time("h:m:s.3 a",curr)
= "7:14:59.224 p"
? time("0h:0m:0s.3 a",curr)
= "07:14:59.224 p"
? time("Current \Mont\h: Month",curr)
= "Current Month: June"See Also
Date and Time Functions
Description
Alpha Anywhere provides the following Date and Time functions.
Overview
C = character
D = Date value (Date variable)
CD = Formatted date (Character variable)
CT = Formatted date time (Character variable)
CY = Formatted time (Character variable)
L = Logical value (Logical variable)
N = Numeric value (Numeric variable)
P = Pointer with dot variables
T = Date time value (Time variable)
Y = Time value (Short time variable)
Arithmetic
- Date Subtraction, + Date Addition
Output: D
Add or subtract a number of days to or from a date to produce a date.
- Date Time Subtraction, + Date Time Addition
Output: T
Add or subtract a number of seconds to or from a date time to produce a date time.
- Time Subtraction, + Time Addition
Output: Y
Add or subtract a number of seconds to or from a short time to produce a short time.
- Date Subtraction
Output: N
Subtract one date from another to produce the interval in days.
- Date Time Subtraction
Output: N
Subtract one date time from another to produce the interval in seconds.
- Time Subtraction
Output: N
Subtract one short time from another to produce the interval in seconds.
Calendars
POPUP.CALENDAR()
Output: C
Displays a calendar and returns a formatted date string.
UI_GET_DATE()
Output: C
Displays a Windows style dialog and returns formatted date string.
UI_GET_DATE_CALENDAR()
Output: C
Displays an HTML formatted dialog and returns a formatted date string.
General
DATE()
Output: D
Returns today's Date.
Date_FirstDayOfMonth()
Output: D
Returns the first date of a month relative to a specified date (default value is today).
Date_FirstDayOfPreviousMonth()
Output: D
Returns the first date of the previous month relative to a specified date (default value is today).
Date_LastDayOfMonth()
Output: D
Returns the last date of a month relative to a specified date (default value is today).
Date_LastDayOfPreviousMonth()
Output: D
Returns the last date of a previous month relative to a specified date (default value is today).
GetTimeZoneOffset()
Output: N
Returns the difference between the computer's time zone and Greenwich Mean Time.
ISDATE()
Output: L
Returns .T. if the character string is a valid representation of a Date value.
IsShortTime()
Output: L
Returns .T. if the character string is a valid representation of a Short Time value.
ISTIME()
Output: L
Returns .T. if the character string is a valid representation of a Time value.
NOW()
Output: T
Returns the current date/time, correct to the millisecond, in the Time data type.
NULL_VALUE()
Output: D
Assigns a NULL value to a date.
A5_GETDATEHTML()
Output: D
Displays a HTML calendar and returns a date.
TZ_OFFSET_TO_C()
Output: C
Calls the GetTimeZoneOffset() function and formats the result as a character string.
WIN_TIME()
Output: P
Returns information about the time settings of a computer.
Calculation Functions
ADD_BUS_DAYS()
Output: D
Adds a specified number of business days ( Add_Days ) to a Starting_Date and returns an Ending_Date.
ADDMONTHS()
Output: D
Returns an Ending_Date equal to the specified Starting_Date plus the specified Number_Of_Months.
ADDYEARS()
Output: D
Returns an Ending_Date equal to the specified Date plus the specified Number_Of_Year s.
AGE()
Output: N
Computes the number of years since a Starting_Date and returns an integer.
BUS_DAYS_BETWEEN()
Output: N
Computes the number of business days between two dates.
Date_FirstDayOfMonth()
Output: N
Given a date, returns the first day of its month.
Date_FirstDayOfPreviousMonth()
Output: N
Given a date, returns the first day of its previous month.
DATE_IS_IN_MONTH()
Output: L
Determines if a Date value is in a specified Month.
Date_LastDayOfMonth()
Output: N
Given a date, returns the last day of its month.
Date_LastDayOfPreviousMonth()
Output: N
Given a date, returns the last day of its previous month.
INCREMENT_VALUE()
Output: D
Increments the date by one.
MONTH_END()
Output: D
Returns the date of the last day of the month in which date occurs.
MONTH_START()
Output: D
Returns the date of the first day of the month in which date occurs.
NTH_DOW()
Output: CD
Returns the date for the Nth occurrence of the specified day of the week starting in the specified month and year.
Conversion Functions
A5_T_FROM_RFCDATE()
Output: T
Converts a date string formatted by A5_ANSIDATE(), A5_RFC1123DATE(), A5_RFC822DATE(), or A5_RFC850DATE() into a time-date value.
CDATE()
Output: D
Converts a Date to a Formatted_Date character string in the form "YYYYMMDD".
CDOW()
Output: C
Returns a character string containing the name of the day of the week for the specified Date.
CMONTH()
Output: C
Returns the Month_Name in the specified Date.
CONVERT_TYPE()
Output: T
Converts variables from one type to another, preserving the data if possible.
CShortTime()
Output: C
Converts a short time value to a sortable character equivalent.
CTIME()
Output: C
Converts a time value to a sortable character equivalent.
CTOD()
Output: D
Converts a character string containing date information to a Date value.
CTODT()
Output: T
Converts a date and time string to a date time value.
CTOT()
Output: Y
Converts a time string to a short time value.
CYEAR()
Output: C
Returns a character string containing the year in the form "YYYY" based on the specified Date_Value.
DATE_FORMAT()
Output: CT
Returns any portion of a Date_Time as a formatted string.
DATE_VALUE()
Output: D
Returns Date_Value for the specified year, month and day.
DAY()
Output: N
Returns an integer corresponding to the day of the month for a given Date or Date_Time.
DAY_NUMBER()
Output: N
Returns the number of a given day name.
DOW()
Output: N
Returns an integer indicating the day of the week for the Date_Value.
DOW_ISO()
Output: N
Returns the ISO day of the week.
JDATE()
Output: N
Converts Date_Value to a Julian date, which is an integer value measured in days from a special starting date.
JTODATE()
Output: D
Converts a Julian date (which is an integer value measured in days) to an Alpha Anywhere Date value.
MONTH()
Output: N
Returns an integer equal to the month number (1-12) of the specified Date or Date_Time.
MONTH_NUMBER()
Output: N
Returns the month number (1 to 12) for a given month name.
ODBC_DT_TO_D()
Output: D
Converts a character Date_Time_String of format "YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.SSS" to a date value.
SCANTIME()
Output: T
Returns a Date_Time_Value in a Time variable by parsing the character date time value specified by Formatted_Date_Time according to the format specified by Format_String.
ShortTime_Extract()
Output: Y
Extracts the hours, minutes, or seconds value from a Short_Time.
STOD()
Output: D
Converts a character representation of a date in the format "YYYYMMDD" into a date.
TIME_VAR()
Output: T
Creates a "time" variable from year, month, day, hour, minute, and second values.
TOSECONDS()
Output: N
Converts a Formatted_Time_String containing a time value to an integer Count equal to the number of seconds past midnight.
WEEK()
Output: N
Returns the number of the week in the year for a date value.
WEEK_ISO()
Output: N
Returns the ISO week number.
WEEK_ISO_FULL()
Output: C
Returns the fully qualified ISO week number.
WMI_DATE_TO_TIME()
Output: T
Converts a CIM date time string as used by WMI to an Alpha Anywhere Date Time value in the local time zone.
YEAR()
Output: N
Returns a four digit integer equal to the year portion of the specified Date or Date_Time.
YearStart_ISO()
Output: D
Returns the first day of the ISO year for a given year.
Formatting Functions
Predefined Date Formats
Predefined date formats for use with functions such as DTOC().
Date and Time Format Elements
Rules for coding date and time formats.
A5_CONVERT_DATE_STRING()
Output: CD
Reformats a date string.
A5_CONVERT_DATETIME_STRING()
Output: CT
Reformats a date time string.
A5_RFC81123DATE()
Output: CT
Takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string, following the RFC 1123 format.
A5_RFC81123DATE()
Output: CT
Takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string, following the RFC 1123 format.
A5_RFC822DATE()
Output: CT
Takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string, following the RFC 822 format.
A5_RFC850DATE()
Output: CT
Takes a date, either as a time or character, and converts it to a string, following the RFC 850 format.
A5_TIMESTAMP()
Output: CY
Returns Formatted_Short_Time containing the system time
DATE_FORMAT()
Output: CD
Creates a formatted character string representation of the Date_Value.
DATE_FORMATS_BUILT_IN()
Displays the Data Format dialog box and returns the number of the selected format.
DMY()
Output: CD
Returns a formatted character string in the DD Month YYYY format for the specified Date_Value.
DTOC()
Output: CD
DTOC()returns a formatted character string for the specified Date or Date_Time value.
DTOS()
Output: CD
Converts a Date_Value to a Formatted_Date character string in the form "YYYYMMDD."
FORMAT_DATA()
Output: CD
Converts a Date_Value to a Formatted_Date character string. Refer to Display Formats.
FixDateString()
Output: CD
Reformats a Formatted_Date character string for web applications.
GMT()
Output: CY
Returns Greenwich Mean Time as a Formatted_Short_Time.
MDY()
Output: CD
Returns a Formatted_Date in the Month DD, YYYY format for the specified Date_Value.
SQL_DATE()
Output: CY
Formats a date value to "{YYYY-MM-DD}".
TIME()
Output: CT
Returns a character string containing a Formatted_Date_Time. If the Date_Time_Value parameter is not specified, the current system time is formatted.
TOTIME()
Output: CY
Returns a Formatted_Short_Time based on the specified Number_Of_Seconds past midnight.
See Also
- Predefined Date Formats
- Date and Time Format Codes
- Date and Time Conversion Matrix
- Date and Time Functions
DATE Function
Syntax
Returns
- todays_dateDate
Returns the current date as a date type.
Description
Returns the current system date.
Discussion
DATE() returns today's date. The system date must be set at the DOS level (use the DOS DATE command). This function is useful for fields that should contain the current date.
Example
Assume that you want to use a range filter in View mode to display only the records for overdue accounts. If your table stores the date that an order was placed in a field called ORDERDATE, the following expression yields the number of days since the order was placed:
date() -ORDERDATE
You can generate a complete filter expression to find all open accounts over 30 days old by adding a check on a BALANCEDUE field. The filter is:
((date() - ORDERDATE) > 30) .AND. (BALANCEDUE > 0)
See Also
Date_FirstDayOfMonth Function
Syntax
Arguments
- First Date
The first date of a month.
- date
Optional. Default = today. The date to use when calculating the first day of the month.
Description
Returns the first day of the month for a given date. If no argument is supplied, first day of current month.
Discussion
The Date_FirstDayOfMonth() function returns the first day of a month.
Example
? Date_FirstDayofMonth()
= {06/01/2006}
? Date_FirstDayofMonth({7/4/06})
= {07/01/2006}See Also
Date_FirstDayOfPreviousMonth Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
Optional. Default = today. The date to use when calculating the first day of the previous month.
Description
Returns the first day of the previous month for a given date. If no argument is supplied, returns last day of the previous month for the current date.
Discussion
The Date_FirstDayOfPreviousMonth() function returns the first day of the previous month.
Example
? Date_FirstDayOfPreviousMonth()
= {05/01/2006}
? Date_FirstDayOfPreviousMonth({7/4/06})
= {06/01/2006}See Also
DATE_FORMAT Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateDate
A representation of a date that satisfies the ISDATE()function.
- formatCharacter
The date format defined using date format elements. See Date and Time Format Elements for more information about defining a format.
Returns
- Formatted_Date_Time_StringCharacter
Returns the formatted date.
Description
Formats a date value using a user defined format string
Discussion
DATE_FORMAT() returns a formatted character string representation of the Date_Value.
Example
dim dateString as C dateString = date_format(DATE() , "MON, d-yyyy") ? dateString = "JAN, 11-2018"
See Also
DATE_FORMATS_BUILT_IN Function
Syntax
Description
Date formats for the dtoc() function
Discussion
The DATE_FORMATS_BUILT_IN() function displays the Data Format dialog box and returns the number of the selected format.
Example
? DATE_FORMATS_BUILT_IN() = "4"
Limitations
Desktop applications only.
See Also
date_from_utc_date Function
Syntax
Arguments
- utcFormat
Character
- ReturnType
Character
Description
Convert a UTC date-time to a date or time
See Also
date_is_anniversary Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
- referenceDate
Date
Description
Returns .t. if a date or time value has the same month and day as a ReferenceDate. If ReferenceDate is blank, then today's date is used as the ReferenceDate.
See Also
date_is_in_last_month Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in the previous Month
See Also
DATE_IS_IN_MONTH Function
Syntax
Result_Flag as L = date_is_in_month(D date ,* month )
Result_Flag as L = DATE_IS_IN_MONTH( date as D, month as C )
Result_Flag as L = DATE_IS_IN_MONTH( date as D, month as N )
Arguments
- date
A date value.
- month
A month expressed as either a character string (e.g. "Feb", "February") or as a number.
Description
True if date is in specified month. Month can be a Character or Numeric value
Discussion
The DATE_IS_IN_MONTH() function determines if a Date value is in a specified Month.
Example
? date_is_in_month({3/15/03}, "February")
= .F.
? date_is_in_month({3/15/03}, 2)
= .F.
? date_is_in_month({3/15/03}, 3)
= .T.
? date_is_in_month({3/15/03}, "Mar")
= .T.See Also
date_is_in_previous_quarter Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in the previous Quarter
See Also
date_is_in_previous_week Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in the week
See Also
date_is_in_previous_year Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in the previous year
See Also
date_is_in_same_week Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
- referenceDate
Date
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in the same week as the week of the reference date
See Also
date_is_in_this_month Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this Month
See Also
date_is_in_this_month_todate Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this Month-to-date
See Also
date_is_in_this_quarter Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this Quarter
See Also
date_is_in_this_quarter_todate Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this Quarter
See Also
date_is_in_this_week Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Returns .t. if the date is in the current week.
See Also
date_is_in_this_week_todate Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this week-to-date
See Also
date_is_in_this_year Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this year
See Also
date_is_in_this_year_todate Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is in this year-to-date
See Also
date_is_today Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is today
See Also
date_is_yesterday Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes a date or time value and returns .t. if the date is yesterday
See Also
Date_LastDayOfMonth Function
Syntax
Arguments
- LastDate
The last date of a month.
- date
Optional. Default = today. The date to use when calculating the last day of a month.
Description
Returns the last day of the month for a given date. If no argument is supplied, last day of current month.
Example
? Date_LastDayofMonth()
= {06/30/2006}
? Date_LastDayofMonth({7/4/06})
= {07/31/2006}See Also
Date_LastDayOfPreviousMonth Function
Syntax
Arguments
- LastDate
The last date of the previous month.
- date
Optional. Default = today. The date to use when calculating the last day of the previous month.
Description
The Date_LastDayOfPreviousMonth() function returns the last day of the previous month for a given date. If no argument is supplied, returns last day of the previous month for the current date.
Example
? Date_LastDayOfPreviousMonth()
= {05/31/2006}
? Date_LastDayOfPreviousMonth({7/4/06})
= {06/30/2006}See Also
date_quarternumber Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
*
Description
Takes as date or time value and returns the Quarter in which the date falls
See Also
date_quarterstartend Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Year
Numeric
- quarter
Numeric
Description
Returns two properties - .StartDate and .EndDate with the start and end date for the specified quarter.
See Also
date_to_utc_date Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateTime
Any type
Description
Convert a date or time to a UTC date-time
See Also
DATE_VALUE Function
Syntax
Arguments
- year
The four digit integer representation of a year. Numeric
- month
The one or two digit integer representation of a month. Numeric
- day
The one or two digit integer representation of a day of the month. Numeric
Description
Returns a date value. Errors if date is out of range
Discussion
DATE_VALUE() returns a Date_Value for the specified year, month and day. This function is useful because it works regardless of what regional settings (e.g. U.S., United Kingdom, etc.) are in effect.
Example
date_value(2000,2,1) -> {2/1/2000} (assuming regional settings are set for the U.S).
date_value(2000,2,1) -> {1/2/2000} (assuming regional settings are set for the U.K).See Also
DAY Function
Syntax
Day_Of_Month as N = DAY( Date as D )
Day_Of_Month as N = DAY( Date_Time as T )
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE(Date) = .T.).
- Date_Time
A variable containing a date-time value (type T).
Description
DAY() returns an integer corresponding to the day of the month for the Date or Date_Time value.
Example
day(START) -> 9, if START contains 07/09/91
day({1/15/2004}) -> 15You can create your own custom date formats for reports, forms, mailing labels, and form letters using a combination of the DAY() , CMONTH(), and CYEAR()functions. For example, to display the BIRTHDATE field as "December 18, 1991" in a form letter, define a calculated field using the following expression:
cmonth(BIRTHDATE) + " " + ltrim( str( day(BIRTHDATE) ) ) + ", " + cyear(BIRTHDATE)
In this expression, DAY() returns the day of the month, STR()converts the number to a character field, and LTRIM()strips off leading blanks. You can also use the MDY()function to return formatted date strings.
MDY(BIRTHDATE) -> "May 25, 1968"
See Also
DAY_NUMBER Function
Syntax
Arguments
- day_name
The name of the week (at least the first three letters).
Description
DAY_NUMBER() returns the number of a given day. You only need to specify the first three characters of the Day_Name. Sunday is 1.
Example
day_number("sunday") -> 1
day_number("mon") -> 2See Also
DMY Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
Date A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
- Date_Time
A variable containing a date time value.
Description
Converts a date to a character string in the 'DD Month YYYY' format.
Discussion
DMY() returns a formatted character string in the "DD Month YYYY" format for the specified Date or Date_Time value.
Example
dmy({12-18-92}) -> "18 December 1992"See Also
DOW Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
- Date_Time
A variable containing a date time value.
Description
DOW() returns an integer indicating the day of the week for the Date or Date_Time value.
- Number
- Day of the Week
- 1
Sunday
- 2
Monday
- 3
Tuesday
- 4
Wednesday
- 5
Thursday
- 6
Friday
- 7
Saturday
Example
dow(START) -> 2 if START contains 11/27/95
dow(CTOD("05/19/95")) -> 6Suppose you want to determine whether orders are entered into the table at a constant rate, or if certain days are busier than others. The table contains a date field, ORDERDATE, indicating when the orders are entered. First, create an index using the expression:
dow(ORDERDATE)
Next, create a report with one level of grouping. For the group break expression, use the same expression. In the Group 1 footer, define and place a calculated summary field that will print a count of the number of records for the current group.
See Also
DOW_ISO Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Day_of_Week
The ISO day of the week (Monday = 1, Sunday = 7).
- date
The date to be analyzed.
Description
Returns the ISO 8601 Day of Week # where Monday is day 1 and Sunday is day 7
Discussion
The DOW_ISO() function returns the ISO day of the week.
Example
? dow_iso(date() ) = 4 ? dow_iso( ctod( "01/19/2006") ) = 4
See Also
DTOC Function
Syntax
dim Formatted_Date as C = DTOC(Date_Value D [, Format as C [, Localized as L]])
dim Formatted_Date as C = DTOC(Date_Value as T [, Format as C])
Arguments
- Date_ValueDate Time
A variable containing a date or date time value.
- FormatLogical
Default = "MM/DD/YYYY". Refer to Predefined Date Formats below.
- localizedLogical
Default = .f.. If true, the date is localized using the regional language setting. This only applies to formats where the name of the month is printed.
Returns
- Formatted_DateCharacter
The Date_Value formatted into a character string.
Description
Converts a date into a character value in the form 'MM/DD/YYYY'.
Discussion
DTOC() returns a character string in the specified Format for the specified Date or Date_Time value. DTOC() is useful for indexing a table when month order is more important than chronological date order (which orders first by year, then month, then day).
If you have a multi-field index involving both date and character fields, use the CDATE() function if you want a chronological date order.
Predefined Date Formats
The following formats can be used with the DTOC() function.
- Format Code
Meaning
- 1-
12-31-2015
- 2-
21-12-2015
- 1/
12/31/2015
- 2/
31/12/2015
- 3
31 December 2015
- 4
December 31, 2015
- 8
December 31st, 2015
- 5-
12-15
- 6-
12-31-15
- 7-
31-12-15
- 5/
12/15
- 6/
12/31/15
- 7/
31/12/15
- 9-
31-Dec-15
- 10
31 Dec 2015
- 11-
15-12-31
- 12-
2015-12-31
- 11/
15/12/31
- 12/
2015/12/31
- 11.
15.12.31
- 12.
2015.12.31
- 3C
31 DECEMBER 2015
- 4C
DECEMBER 31, 2015
- 8C
DECEMBER 31ST, 2015
- 9C-
31-DEC-15
- 10C
31 DEC 2015
Examples
dim now as D
now = now()
? now
= {12/12/2017}
? dtoc(now)
= "12/12/2017"
? dtoc(now,"12.")
= "2017.12.12"
? dtoc(now,"10",.f.)
= "12 Dec 2017"
' System Locale is set to France (Belgium):
? dtoc(now,"10",.t.)
= "12 déc 2017"
dim now2 as T
now2 = now()
? now2
= 12/12/2017 10:58:20 01 am
? dtoc(now2)
= "12/12/2017"
? dtoc(now2,"6-")
= "12-12-17"
? dtoc(now2,"4C",.f.)
= "DECEMBER 12, 2017"
' System Locale is set to France (Belgium):
? dtoc(now2,"4C",.t.)
= "DéCEMBRE 12, 2017"See Also
DTOS Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Date_Time_ValueDate
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value (ISDATE(Date_Value) = .T.).
Returns
- Formatted_DateCharacter
The Date_Value formatted into a character string.
Description
Converts a date into a character value in the form 'YYYYMMDD'.
Discussion
DTOS() converts a Date_Time_Value to a Formatted_Date character string in the form "YYYYMMDD." This function is useful for constructing multi-level indexes that contain both character and date fields.
Indexes containing the DTOS() function order dates chronologically (year, then month, then day), while those containing DTOC() order dates by month, day, and year.
Examples:
INV_DATE = {12/18/1993}
? dtos(INV_DATE)
= "19931218"Assume you want to order an employee table by department and within each department by seniority. The table has a character field, DEPT, and a date field, STARTDATE. Use the following index expression:
DEPT + dtos(START)
The following Employee table shows the order created by this index:
FIRSTNAME | DEPT | START |
|---|---|---|
Steve | Marketing | 03/21/78 |
Kate | Marketing | 04/17/79 |
Janice | Marketing | 01/02/83 |
Ralph | R&D | 01/01/80 |
Tim | R&D | 03/20/80 |
Francie | R&D | 02/17/84 |
Compare this result with the DTOC() function. If the DTOC() function is used in the above index expression instead of DTOS(), the following ordering results:
FIRSTNAME | DEPT | START |
|---|---|---|
Janice | Marketing | 01/02/83 |
Steve | Marketing | 03/21/78 |
Kate | Marketing | 04/17/79 |
Ralph | R&D | 01/01/80 |
Francie | R&D | 02/17/84 |
Tim | R&D | 03/20/80 |
Entering search criteria to search on a date field presents a problem because you cannot type in a date directly as a text string. You must either surround the text you enter with the CTOD() function, or use a function to convert the date field to a character field before comparing it with the text.
If you want to search a date field, BIRTHDAY, for the date, "September 20, 1966," you can enter the following criteria:
dtos({09/20/66}) -> 19660920
dtos(BIRTHDAY) = "19660920" or
BIRTHDAY = ctod("09/20/1966") or
BIRTHDAY = ctod("09/20/66") or
BIRTHDAY = {9/20/66}See Also
FixDateString Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Formatted_Date
A new version of the date with rearranged day, month, and year values.
- dateString
A date string containing day, month, and year values.
- dateFormat
A character string containing "D", "M", and "Y" separated by a delimiter.
Description
Takes a date string and a date format and transforms the date string so that it matches the format that Alpha Anywhere expects (based on the current Regional Settings configuration). The year portion MUST be the last part of the date format. I.e. Does not support formats like YYYY/mm/dd
Discussion
This function is only of use to users outside the United States who are hosting their web applications on servers in the United States, where the date format on the server does not match the date format that users of the application will be using. The function is useful in custom Xbasic pages. It takes a date string and converts it into a new date string that is based on the regional settings of the machine where Alpha Anywhere is running.
Example
For example, if the server is running on a computer that expects dates to be in M/D/Y format and the user is in the UK where the date format is D/M/Y then:
? fixDateString("31/12/04","d/m/y")
= "12/31/04"See Also
FORMAT_DATA Function
Syntax
Result_String as C = FORMAT_DATA( Input_Value as C, Format_Code as C)
Result_String as C = FORMAT_DATA( Input_Value as D, Format_Code as C )
Result_String as C = FORMAT_DATA( Input_Value as L, Format_Code as C )
Result_String as C = FORMAT_DATA( Input_Value as N, Format_Code as C [, Field_Width as N [, Field_Decimal as N ]] )
Arguments
- input_valueCharacter Date Logical Numeric
The value to format.
- format_codeCharacter
A format string. Refer to Display Formats.
- fld_widthNumeric
Default = 20. The maximum expected length of the formatted string. Value must be larger than the length of the formatted string. For numeric values only.
- fld_decNumeric
Default = 2. The number of characters after the decimal point. Output will be padded with zeros. For numeric values only.
Description
Formats an input string using a format_code. Returns a character string.
Discussion
The FORMAT_DATA() function formats a character, date, numeric, or logical value. For numeric inputs, FORMAT_DATA() is the same as calling ALLTRIM(STR(...)).
? format_data("edwaRd","Z")
= "Edward"
? format_data(date(),"3C")
= "16 MARCH 2017"
? format_data(.t.,"2")
= "Yes"
? format_data(1234567.89,",B*")
= "********1,234,567.89"
dim nn as N
nn = 12345678900000.456
? format_data(nn,"$",22)
= "$12,345,678,900,000.46"See Also
GetTimeZoneOffset Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Offset
The difference between the time zone of the computer and Greenwich time in hours.
Description
The GetTimeZoneOffset() function returns difference between the time zone of the computer and Greenwich Mean Time in hours.
Returns the number of hours the current timezone is offset from GMT.
Example
? gettimezoneoffset() = -5
See Also
GMT Function
Syntax
Arguments
- time_format
Optional. Default = "hh:mm:ss". The format for the time value. Character
Description
GMT() returns Greenwich Mean Time on the system clock as a Formatted_Short_Time ('HH:MM:SS'). For information on the optional Format_String parameter.
Example
put description here
gmt() -> "19:31:18"
See Also
Holidays
Description
This panel lets you enter holidays to be used in your Alpha Anywhere databases.
One of the most useful functions of entering holidays is that when Alpha Anywhere computes the number of business days between two dates, the holidays listed here will not be counted. For example:
ADD_BUS_DAYS() BUS_DAYS_BETWEEN()
To add a holiday, click the Add button. You will be prompted for the name and date of the holiday.
To remove a holiday, highlight the holiday in the list and click the Remove button.
To change the name or date of a holiday you have already entered, highlight the holiday in the list and click the Edit button. You will be prompted again for the name and date.
The Sort by name and Sort by date radio buttons will sort the list accordingly. This can be useful if you are looking for a specific holiday.
See Also
httpdate Function
Syntax
DateStr as C = httpdate(date as C)
DateStr as C = httpdate(date as D)
DateStr as C = httpdate(date as T)
Arguments
- dateCharacter Date Time
The date to convert. The date can be specifeid as a Date, Datetime, or Character object.
Returns
- DateStrCharacter
An HTTP compliant formatted date/time string.
Description
Creates an HTTP compliant date/time string
Example
'Converting date string to HTTP Date
dim todayC as C = "2/23/2017 11:06 AM"
? todayC
= "2/23/2017 11:06 AM"
? httpdate(todayC)
= "Thu, 23 Feb 2017 16:06:00 GMT"
'Converting date to HTTP Date
dim todayD as d = date()
? todayD
= {02/23/2017}
? httpdate(todayD)
= "Thu, 23 Feb 2017 05:00:00 GMT"
'Converting Datetime to HTTP Date
dim todayDT as T = now()
? todayDT
= 02/23/2017 11:06:22 01 am
? httpdate(todayDT)
= "Thu, 23 Feb 2017 16:06:22 GMT"international_days_of_week Function
Syntax
Arguments
- C Result =
Days of the week, one per line
- options
(optional) Comma-delimited list of parameter-value expressions, such as: language=cultureCode, short, shortest, start-dayName
Description
Returns day of week, using current culture settings
Example
? international_days_of_week()
= Sunday
Monday
...
? international_days_of_week("start-monday,shortest")
= Mo
Tu
...
' german
? international_days_of_week("language=de")
= Sonntag
Montag
..The months and days returned are in UTF8 , so when dealing with the Web applications, you can take the output as is. However, when working from a desktop application (which assumes ACP) , you will need to call convert_utf8_to_acp()
See Also
international_months Function
Syntax
Arguments
- result
Names of months, one per line
- options
(optional) Comma-delimited list of parameter-value expressions, such as: language=cultureCode, short, shortest
Description
Returns name for all months, using current culture settings
Example
? international_months()
= January
February
...
' spanish
? international_months("language=es")
= enero
febrero
...See Also
JDATE Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
Optional. Default = DATE(). A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE ( Date_Value ) = .T.).
Description
Returns a number which is the Julian equivalent to a specified date.
Discussion
JDATE() returns the integer Julian date equivalent of Date_Value. The Julian date is an integer value measured in days from a special starting date. You can use the resulting value with other numeric values to do special computations on dates. For example, to compute the "day of the year", use this expression: JDATE( Date_Value ) - JDATE(CTOD("1/1/" + YEAR( Date_Value ))) + 1.
Example
?jdate({1/5/95})
= 2449723
?jdate({3/10/95})
= 449787
' computes the "day of the year" assuming today is 7/12/99
? jdate() - jdate({1/1/99})
= 192The following expression returns the day of the year.
? jdate( date() )-jdate( ctod( "01/01/"+cyear( date() ) ) ) + 1 = 327
See Also
JTODATE Function
Syntax
Arguments
- number
An integer value representing a Julian date, as Produced by the JDATE() function. Numeric
Description
Returns a date value which is the equivelant to the supplied Julian number.
Discussion
JTODATE() converts a Julian date (which is an integer value measured in days) to an Alpha Anywhere Date value. After you have used JDATE() to convert dates to numbers (in order to perform computations on them), you can use JTODATE() to display the results as Dates. NOTE: JDATE() now returns values in a numeric format compatible with input to JTODATE(). For example, if the current date is 9/21/1995, then:
? jdate({09/21/1995})
= 2449982.000000
? jtodate(2449982.000000)
= {09/21/1995}Example
' if the current date is 9/21/1995
? jtodate( jdate( DATE() + 7) )
= {09/28/1995}How to Import a Julian Date
A Julian date is a number cannot be imported directly into a date field. To import a julian date:
- 1.
Import the Julian date data into a numeric field (e.g. numeric_field ).
- 2.
Select the Operation tab of the Control Panel.
- 3.
On the Create New Operation dialog box, select "Update Records" from the Select Operation list.
- 4.
Select your table from the Select Table/Set list.
- 5.
Click Create Using Genie.
- 6.
Click the General tab.
- 7.
Select "Assign a Calculated Value to a Field" and click Next >.
- 8.
Select the date field (e.g. date_field ) of your table in the Which field would you like to update? list.
- 9.
Enter the expression jtodate(numeric_field) in the Enter the expression for the calculated value field.
- 10.
Click Next >, Next >, Next >, and Finish.
- 11.
Enter a name for the operation and click OK, OK, and OK.
See Also
MDY Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
Description
Returns a formatted character string in the 'Month DD, YYYY' format.
Discussion
MDY() returns a Formatted_Date in the "Month DD, YYYY" format for the specified Date_Value.
Example
mdy({12-18-95}) -> "December 18, 1995"
mdy(BIRTHDAY) -> "November 25, 1995", assuming BIRTHDAY contains 11-25-95
mdy(date() )-> Current system dateSee Also
MONTH Function
Syntax
Month_Number as N = MONTH( Date as D)
Month_Number as N = MONTH( date_time as T)
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE ( Date_Value ) = .T.).
- date_time
A variable containing a date-time value (type T).
Description
Returns the number of the month in a date.
Discussion
MONTH() returns an integer equal to the month number (1-12) of the specified Date or Date_Time value..
Example
month(START) -> 3, if START contains 03/10/88 month( ctod( "12/12/88") ) -> 12
The following example computes the current quarter.
ceiling(month(date() )/3)
See Also
MONTH_END Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
A date constant or variable.
Description
Computes the date on which a month ends for any given date.
Discussion
MONTH_END() returns the date of the last day of the month in which date occurs.
Example
? month_end({7/12/2002})
= {7/31/2002}See Also
MONTH_NUMBER Function
Syntax
Arguments
- month
The English name of a month. The MONTH_NUMBER() function is case insensitive. Character
Description
Returns the month number for a given month name
Discussion
MONTH_NUMBER() returns the month number (1 to 12) for a given month name. Returns 0 when the Month_Name expression cannot be interpreted.
Example
month_number("ApRil") -> 4.000000
month_number("January 20, 1950") -> 1.000000
month_number("1/20/50") -> 0.000000See Also
MONTH_START Function
Syntax
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
Description
Computes the date on which a month starts for any given date.
Discussion
MONTH_START() returns the date of the first day of the month in which date occurs.
Example
month_start({7/12/2002} -> {7/1/2002}put description here
See Also
NOW Function
Syntax
Arguments
- gmt_timeLogical
Default = .F. If flag is .T., then the time is returned as GMT. If flag is .F., time is returned as the local system time.
Returns
- Date_TimeTime
Returns the current date and time as a time data type.
Description
Returns the current time. The time can be returned as either local time (default) or GMT.
Discussion
NOW() returns the current date and time, correct to the millisecond, in the Time data type. The time can be returned as either local time or GMT time.
If used in a web application and the local time is returned, the time will be calculated using the web application server's system time.
? now() = 01/16/2003 10:24:51 09 am ' Return time as GMT ? now(.T.) = 01/16/2003 03:24:51 09 pm dim t1 as T dim t2 as T t1 = now() t2 = now() ? t2-t1 = 5.440000
Comparing NOW() with TIME()
Both the NOW() and TIME() function will return the current time. The difference between the two methods is that NOW() returns the current time as a time type while TIME() returns a character string. As a result, if you try to assign the value returned by the TIME() function into a time variable, a "variable type mismatch" error will occur:
dim t3 as T ' the following assignment will cause an error because the time function ' returns a character string, not a time value: t3 = time() ERROR: variable type mismatch
The TIME() function also does not return millisecond.
The TIME() function can also be used to format an existing time value. For example:
? time("MM/dd/yyyy 0h:0m:0s 2 am", now(.T.))
= "01/16/2003 03:24:51 09 pm"See Also
NTH_DOW Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dayName
Case insensitive English name or abbreviation for the day of the week.
- month
1 (January) through 12 (December)
- year
Four digit year (1998). Numeric
- occurrence
A positive integer. Numeric
Description
Finds the date for the 'n'th day in a month. e.g. the 4th Thursday for November in 2005
Discussion
NTH_DOW() returns the date for the Nth occurrence of the specified day of the week starting in the specified month and year.
Example
dim cs as C
cs = nth_dow("friday", 12, 1999, 2)
cs -> "{12/10/1999}"
cs = nth_dow("friday", 12, 1999, 8)
cs -> "{01/21/2000}"
cs = nth_dow("mon",12,2002,0)
cs -> " { / / }"See Also
ODBC_DT_TO_D Function
Syntax
Arguments
- odbc_datetime
Date time string in the format "YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.SSS". Character
Description
Converts a character field containing a Date-Time value in format "YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.SSS" to a date field.
Discussion
ODBC_DT_TO_D() converts a character Date_Time_String of format "YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS.SSS" to a date value. This function is useful when you link to an ODBC data source that has a date/time field. Since Alpha Anywhere does not have the corresponding field type, the data is displayed as a character value. Use this function to create a calculated field that extracts just the date portion of the date-time value.
Example
odbc_dt_to_d("2003-01-15 11:46:30.003") -> {01/15/2003}See Also
Predefined Date Formats
Description
The following formats can be used with the DTOC() function.
Predefined Date Formats
- Format Code
- Meaning
- 1-
12-31-2015
- 2-
21-12-2015
- 1/
12/31/2015
- 2/
31/12/2015
- 3
31 December 2015
- 4
December 31, 2015
- 8
December 31st, 2015
- 5-
12-15
- 6-
12-31-15
- 7-
31-12-15
- 5/
12/15
- 6/
12/31/15
- 7/
31/12/15
- 9-
31-Dec-15
- 10
31 Dec 2015
- 11-
15-12-31
- 12-
2015-12-31
- 11/
15/12/31
- 12/
2015/12/31
- 11.
15.12.31
- 12.
2015.12.31
- 3C
31 DECEMBER 2015
- 4C
DECEMBER 31, 2015
- 8C
DECEMBER 31ST, 2015
- 9C-
31-DEC-15
- 10C
31 DEC 2015
Example
dim dd as D dd = date() ? dtoc(dd,"1-") = "01-06-2004" ? dtoc(dd,"4") = "January 6, 2004"
See Also
ProgressTimed Function
Syntax
Arguments
- seconds
The number of seconds until the progress bar completes. Numeric
Description
Displays a progress bar for the specified number of seconds.
Discussion
The ProgressTimed() function displays a progress dialog box that completes in Specified seconds.
The following script displays a progress bar that completes in 10 seconds.
progresstimed(10)
Limitations
Desktop applications only.
See Also
SCANTIME Function
Syntax
Arguments
- time_str
A properly formatted date/time value as specified by Time Format Codes and Year, Month, Day, and Week Format Codes. Character
- Format
A date/time format as specified by Time Format Codes and Date Format Codes. Character
- oldtime
Type
Description
Converts time string to time - uses format to parse the time - optional third parameter is old time to get non-specified values from.
Discussion
SCANTIME() returns a Time variable, by parsing the date time value specified by Formatted_Date_Time according to the format specified by Format_String. Refer to Time Format Codes.
Example
time("dd/MM/yyyy") -> "26/08/1999"
scantime("26/08/1999", "dd/MM/yy") -> 08/26/199912:00:00 00 am
time("X of Month yyyy") -> "Twenty Sixth of August 1999"
scantime("Twenty Sixth of August 1999", "X of Month yyyy") -> 08/26/199912:00:00 00 am
TimeVal = scantime("26/08/1999", "dd/MM/yy")
typeof(TimeVal) -> "T"See Also
ShortTime_Extract Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Result
The number of time units specified in Time_Part.
- shortTime
The short time value to analyze.
- TimePart
The part of the short time value to return. "h" = hours, "m" = minutes, "s" = seconds
Description
Extracts hours, minutes, or seconds from a Short time value. TimePart is 'h', 'm', or 's'
Discussion
The ShortTime_Extract() function extracts the hours, minutes or seconds from a short time value.
Example
dim st as Y
st = ctot("8:32 45.345 pm")
? shortTime_extract(st,"h")
= 20
? shortTime_extract(st,"m")
= 32
? shortTime_extract(st,"s")
= 45.345
? if(shortTime_extract(st,"h") > 11, "pm", "am")
= "pm"See Also
STOD Function
Syntax
Arguments
- cDateCharacter
A character representation of a date in the format YYYYMMDD.
Returns
- DDateDate
A date value.
Description
Convert a date in YYYYMMDD format to {MM/DD/YYYY}
Discussion
The STOD() function converts a character representation of a date into a date value. STOD() generates an error if the input is invalid.
Example
dim char_date as C = "19500512"
? stod(char_date)
= {05/12/1950}See Also
Time and Date Functions
Description
Descriptions and examples of time and date functions.
Create a new A5W page with the following content.
<%a5 dim ultext as C = "Four score and seven years ago" dim extraspaces as C = " Four score " dim allcaps as C = "SEVEN YEARS AGO" %> <html> <head> <meta name="generator" content="Alpha Anywhere HTML Editor"> <title>Date and Time Functions</title> </head> <body> <br> <h1><font face=Verdana color=#0000ff>Date and time functions</font></h1> <font face=Verdana size=2><ul> <%a5 ? "<li>ADD_BUS_DAYS()computes a new date. For example ADD_BUS_DAYS({1/1/84},180) adds 180 business days to 1/1/84, producing " + ADD_BUS_DAYS({1/1/84},180) + "<br>" ? "<li>ADDMONTHS()computes a new date. For example ADDMONTHS({1/31/84},3) adds 3 months to 1/31/84, producing " + ADDMONTHS({1/31/84},3) + "<br>" ? "<li>DATE()returns today's date. For example DATE()returns " + DATE()+ "<br>" ? "<li>DATE_VALUE()returns a computed date. For example DATE_VALUE(2004, 8, 23) returns " + DATE_VALUE(2004, 8, 23) + "<br>" ? "<li>DTOC()produces a formatted date. For example, DTOC(DATE(),\"4\") produces " + DTOC(DATE(),"4") + "<br>" ? "<li>NOW()returns the current date and time, but the default HTML presentation of NOW()returns " + NOW()+ "<br>" ? "<li>TIME()returns the current system time. For example TIME()returns " + TIME()+ "<br>" ? "<li>TOTIME()returns a formatted time based on the number of seconds past midnight. For example TOTIME(12400,12,0) returns " + TOTIME(12400,12,0) + "<br>" %> </ul></font> <font face=Verdana>Check out <a href="sys_resolve_url("https://documentation.alphasoftware.com/documentation/pages/index?search=Date%20and%20Time%20Functions")"> <font face=Verdana>Date and Time Functions</a> for more information.</font> </body> </html>Note in this example.
You must surround a date value expressed in numbers with "{}".
HTML displays a Time value (which contains both date and time) as a date only.
There are multiple built-in date and time formats. The TOTIME(12400,12,0) function uses format 12. The DTOC(DATE(),"4") function uses format "4".
Alpha Anywhere has more than 50 character manipulation for computing, formatting, and displaying date and time values.
Click File > Save As to save your page as "Date and Time Functions".
Click the 'lightning' icon to run the page in Live Preview. The result should look like this.
- Function
- Description
- ADD_BUS_DAYS()
Adds or subtracts days to a date to return a new date.
- ADDMONTHS()
Adds or subtracts months from a date to return a new date.
- DATE()
Returns today's date.
- DATE_VALUE()
Returns a date based on year, month, and day numbers.
- DTOC()
Formats a date value.
- NOW()
Returns the current date and time.
- TIME()
Returns the current system time.
- TOTIME()
Returns a time value based on the number of seconds past midnight.
TIME Function
Syntax
Arguments
- time_formatCharacter
Optional. Default = "0h:0m:0s". A time format created according to the rules of Date and Time Format Elements.
- timeTime
Default = NOW(). A time value to format.
Returns
- Formatted_Date_TimeCharacter
Returns the current time as a formatted character string.
Description
Returns the current time on the system clock as a string value using the format 'HH:MM:SS', optional format controls other times, passed in time type can be used in place of the current time.
Discussion
TIME() returns a date time value containing a formatted Date Time value. If time_format is not specified, the time is returned in the format HH:MM:SS. The system time is obtained from the system clock (which can be set from DOS).
For information on performing time arithmetic, see the TOSECONDS() and TOTIME() functions.
The optional time_format parameter allows you to create custom date and time formats.
Example
? time("0h:0m:0s:2")
= "02:02:30:22"
? time("h:0m:0s:2")
= "2:02:30:22"
? time("0h:0m:s:2 AM")
= "02:02:30:22 AM"
? time("Weekday Month x, yyyy")
= "Friday January 29th, 1999"
? time("dd-Mon-yy")
= "29-Jan-99"Converting a Time value to a Character value:
? time("",now())
= "01/11/2018 11:53:46 21 am"
? t1
= 01/11/2018 11:55:11 02 am
? time("0h-0m-0s.2", t1)
= "11-55-11.02"See Also
time_gmt_to_local Function
Syntax
dim result as T = time_gmt_to_local(T timeVal [,N offset])
Arguments
- timeValTime
GTM time value to convert.
- offsetNumeric
The number of minutes that local time is after/before GMT. E.g. if the local time zone is GMT-4, the offset would be -4 * 60 or -240.
Returns
- resultTime
Returns the GMT time converted to local time.
Description
Converts GMT time to local time.
Discussion
The time_gmt_to_local() function converts a time value in GMT to local time. The local time is determined by the offset.
In a web application that makes Ajax callbacks, the request automatically includes the offset value for the client. If this function is called in server-side code as part of an Ajax callback, it is not necessary to pass in a value for the offset.
Example
dim offset as N = getTimeZoneOffset() ? offset = -4 ? time_gmt_to_local(now(), offset * 60) = 09/18/2020 11:14:23 40 am
See Also
time_to_unixtimestamp Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timevalueTime
A time value to convert to a Unix timestamp.
Returns
- ResultNumeric
Returns a Unix timestamp value.
Description
Converts a time value to a Unix timestamp value.
A unix timestamp is typically referred to as "Epoch" time, and is normally calculated from GMT (or UTC time), so the time passed into the function should be GMT time to get Epoch time.
Example to get current Epoch time:
dim currTime as T dim getGMTTime as L getGMTTime = .T. currTime = now(getGMTTime) ? currTime = 03/20/2017 10:07:39 45 pm ? time_to_unixtimestamp(currTime) = 1490047659.459
See Also
TIME_VAR Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Date_Time_Value
A Time variable with the specified date time value.
- year
The four digit year. Numeric
- month
The number of the month (January = 1). One or two digits. Numeric
- day
The day of the month. One or two digits. Numeric
- hour
The hour of the day (noon = 12). One or two digits. If you use a 12 hour notation, use the AM_PM field to specify before or after mid-day. Numeric
- minutes
The minute of the hour. One or two digits. Numeric
- seconds
The seconds of the minute. Decimal values are allowed. Numeric
- am_pm
Specifies before or after mid-day. Character. Optional. "a" = before mid-day, "p" = after mid-day
Description
Returns a time variable
Discussion
The TIME_VAR() function creates a date time variable (type T). This function is very useful when you want to compute the elapsed time between two date time values that cross date boundaries.
Example
? Time_Var(2003,5,15,12,55,30.523,"a") = 05/15/2003 12:55:30 52 am ? typeof(Time_Var(2003,5,15,12,55,30.523,"a")) = "T" ? Time_Var(2003,5,15,22,55,30.523) = 05/15/2003 10:55:30 52 pm
put description here
See Also
timez Function
Syntax
Arguments
- time_format
Character
- time
*
Description
Same as time(), but returns a null string if time is a null value.
See Also
TOSECONDS Function
Syntax
Arguments
- character
A time value in one of the following formats:"h:m:s am/pm", "h:m:s", "h:m"
Description
Converts a time value to seconds.
Discussion
Converts a Formatted_Time containing a time value to an integer Count equal to the number of seconds past midnight. You typically use TOSECONDS() to perform time arithmetic to compute the elapsed time between a starting and ending time, or to compute an ending time from a start time and an elapsed time. The TOSECONDS() function supports fractional seconds, e.g. toseconds("3:23:05.23 pm").
Example
toseconds("23") -> 23
toseconds("12:23") -> 44,580
toseconds("2:3:15") -> 7,395
toseconds("2:3:15 PM") -> 50,595Assume you stored the time at which an event started in a field called START, and the time at which the event ended in a field called end. To compute the duration of the event, you use the following expression:
toseconds(end) - toseconds(START)
See Also
TOTIME Function
Syntax
Arguments
- secondsNumeric
The number of seconds past midnight.
- format_codeNumeric
One of the following formats.
- Format Parameter Value
Format
- 0
ss
- 1
hh:mm
- 2
hh:mm:ss
- 3
ddd:hh:mm:ss
- 11
hh:mm AM/PM
- 12
hh:mm:ss AM/PM
- 13
ddd:hh:mm:ss AM/PM
- decimal_placesNumeric
The number of decimal places for seconds. The integer value can be from 0 to 3.
Returns
- Formatted_Short_TimeCharacter
Returns the formatted time value.
Description
Converts a time value to a formatted time character string.
Discussion
TOTIME() returns a formatted character string containing a time based on the specified number of seconds past midnight. The resulting formatted string can be in one of seven formats specified by the format code, and can contain up to three decimal places for seconds.
Example
? totime(125, 2, 0) = "0:02:05" ? totime(863.5, 12, 1) = "0:14:23.5 AM"
You may often need to compute an event's ending time, given the event's start time and duration. For example, assume that an event's start time is stored in START and the event duration (expressed as hh:mm) is stored in DURATION. You can use the following expression to return the time that the event ended:
totime((toseconds(START) + toseconds(DURATION), 1, 0)
If you have imported a time value from Microsoft Excel as a character or numeric value and you wish to convert it to a Short Time value, the following expressions will do the job.
dim dat as C dat = .345 ? totime((val(dat) * 86400),1,0) = "8:17" dim dat2 as N dat2 = .345 ? totime(dat2 * 86400,1,0) = "8:17"
See Also
TZ_OFFSET_TO_C Function
Syntax
Returns
- OffsetCharacter
The difference between the computer's time zone and Greenwich Mean Time in hours.
Description
The TZ_OFFSET_TO_C() function calls the GetTimeZoneOffset()function and formats the result as a character string.
Example
? tz_offset_to_c() = "-0500"
See Also
unixtimestamp_to_time Function
Syntax
Arguments
- timestamp
Numeric
Description
Converts a Unix timestamp number (seconds since 1970-1-1) to a time value
See Also
WEEK Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Date_ValueDate
The date used to determine the calendar week of the year.
Returns
- Week_NumberNumeric
Returns an integer equal to the week number (1-53) for the specified Date_Value.
Description
Get the calendar week number of a date where Sunday is the first day of the week.
Discussion
The WEEK() function returns the integer equal to the week number (1-53) for the specified Date_Value. Every week starts on Sunday. A week includes any number of days in the year. For example, if January 1 is on a Saturday, it is in week 1. January 2 (a Sunday) would be in week 2.
Example
The following example is from the Interactive Window in Alpha Anywhere.
dim start as D = {1/1/2005}
? week(start)
= 1
dim date as D
date = ctod("12/27/04")
? date
= {12/27/2004}
? week(date)
= 53See Also
WEEK_ISO Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateDate
The date to be analyzed.
Returns
- Week_NumberNumeric
Returns the ISO week number of the year where Monday is the first day of the week. Dates at the beginning or end of a calendar year may be included in the week for the previous or next year, respectively.
Description
Get the ISO calendar week number for a date where Monday is the first day of the week.
Discussion
The WEEK_ISO() function returns the ISO 8601 week number of the year where Monday is the first day of the week. Week numbers are 1 to 52 or 53. Part of week 1 may include dates from the previous calendar year. Part of week 52 or 53 may include dates from the next calendar year.
The first week of the year is calculated as the week containing the first Thursday of the calendar year. This implies the following:
- The first week is mostly within the calendar year.
- The first week contains January 4th.
- The first week starts with the Monday nearest January 1st.
The last week of the year is the week containing the last Thursday of the calendar year. The following statements are also true of the last week of the year:
- The last week of the year is mostly within the calendar year.
- The last week contains December 28th.
- The last week ends with the Sunday nearest to December 31st.
dim start as D = {1/1/2005}
? cdow(start)
= "Saturday"
? week_iso(start)
= 53
? week_iso(start+1)
= 53
? week_iso(start+2)
= 1
? cdow(start+2)
= "Monday"See Also
WEEK_ISO_FULL Function
Syntax
Arguments
- dateDate
The date to be analyzed.
Returns
- ISO_WeekCharacter
Returns the fully qualified ISO week in the format "YYYY-W##-d" where "YYYY" is the year, "W##" is the week number (01-53), and d is the day of the week (1-7).
Description
Get the full ISO week in the format "YYYY-W##-d" where YYYY is the year, W## is the week number, and d is the day of the week.
Discussion
The WEEK_ISO_FULL() function returns the full ISO week format "YYYY-W##-d". This format indicates the year, ISO week number, and day of week for a specified date. For example, consider the date June 11, 2012:
dim date as d = {7/11/2012}ISO_WEEK_FULL() returns the following string for this date:
? week_iso_full(date) = "2012-W28-3"
From this string, we can determine the following information about June 11, 2012:
- June 11, 2012 belongs to a week in the year 2012.
- June 11, 2012 falls in week 28 of the calendar year.
- June 11, 2012 is the third day of the week.
If a date falls at the end or beginning of a year, it may be contained in the week of the adjacent year. WEEK_ISO_FULL() can be used to determine if the week for a date at the beginning or end of the year belongs to a different calendar year:
' January 3, 1999 is the last day in week 53 for the 1998 calendar year:
? week_iso_full({1/3/1999})
= "1998-W53-7"
? week_iso_full({1/4/1999})
= "1999-W01-1"
' December 29, 2003 is the first day in week 1 for the 2004 calendar year:
? week_iso_full({12/29/2003})
= "2004-W01-1"
? week_iso_full({12/28/2003})
= "2003-W52-7"See Also
WIN_TIME Function
Syntax
Arguments
- P
A pointer variable containing information about the time settings of a computer.
- computer
Optional. Default = "." (local computer). The name of the computer to analyze.
Description
The WIN_TIME() function returns information about the Windows time settings of a computer.
Discussion
Example
? win_time() = Day = 23 DayOfWeek = 4 Hour = 17 Milliseconds = Minute = 18 Month = 6 Quarter = 2 Second = 23 WeekInMonth = 4 Year = 2005
Limitations
Legacy: This function does not work with Windows 98 and Windows ME.
See Also
WMI_DATE_TO_TIME Function
Syntax
Arguments
- Local_Date_Time
Local date and time.
- Formatted_CIM_Date_Time
Formatted CIM Date time string.
- Local_Time_Zone
Local time zone.
Description
Legacy. Converts a CIM Date Time string
Discussion
The WMI_DATE_TO_TIME() function converts a CIM Date Time string as used by WMI to an Alpha Anywhere Time value in the local time zone. This is a replacement for WMI's SWbemDateTime object because that object is only available on Windows XP and Windows 2003. The WMI CIM format is yyyymmddHHMMSS.mmmmmmsUUU.
Example
? wmi_datetime_to_time("20040616180931.990000-240", a5_os_info().CurrentTimeZone)
= 06/16/2004 06:09:31 00 pmSee Also
wmi_datetime_to_time Function
Syntax
Arguments
- wmitime
Character
- gmt_offset
Numeric
Description
Converts a CIM Datetime string as used by WMI to an Alpha Anywhere time value in the local timezone
See Also
YEAR Function
Syntax
Year as N = YEAR( Date as D )
Year as N = YEAR( Date_Time as T )
Arguments
- date
A variable containing a date value or a character string containing a legitimate representation of a date value ( ISDATE (Date_Value) = .T.).
- Date_Time
A variable containing a date-time value (type T).
Returns
- YearNumeric
Returns the full year for the specified date.
Description
Returns a four digit integer equal to the year portion of the specified Date or Date_Time value.
Discussion
Example
If START contains 05/25/1995.
? year(START) = 1995 ? year(date() ) = 2006 ? year(now() ) = 2006
Two Digit Years
If the date specifies the year using two digits, the YEAR() function will assume the date to be in the 20th century if it is on or after '00' to an upper bound defined in the Settings for Alpha Anywhere.
For example:
? year({10/20/30})
= 1930
? year({01/02/03})
= 2003You can change the upper bound for two digit years assumed to be 21st century years in the Alpha Anywhere Development Environment settings. Under the View menu, select Settings. Open the Date settings and change the upper bound for two digit years assumed to be 21st century years.
You can optionally require all years to be 4 digit years in dates by checking Require all years to be fully specified.
See Also
YearStart_ISO Function
Syntax
Arguments
- First_Week
The first day of the ISO year for a given year. Numeric
- WhichYear
The date to be analyzed. Numeric
Description
The YearStart_ISO() function returns the first day of the ISO year.
Discussion
Example
? yearstart_iso(2005)
= {01/03/2005}
? yearstart_iso(2004)
= {12/29/2003}put description here
See Also